Understanding the Implications of Vietnam’s Proposed E-Cigarette Tax Regulations
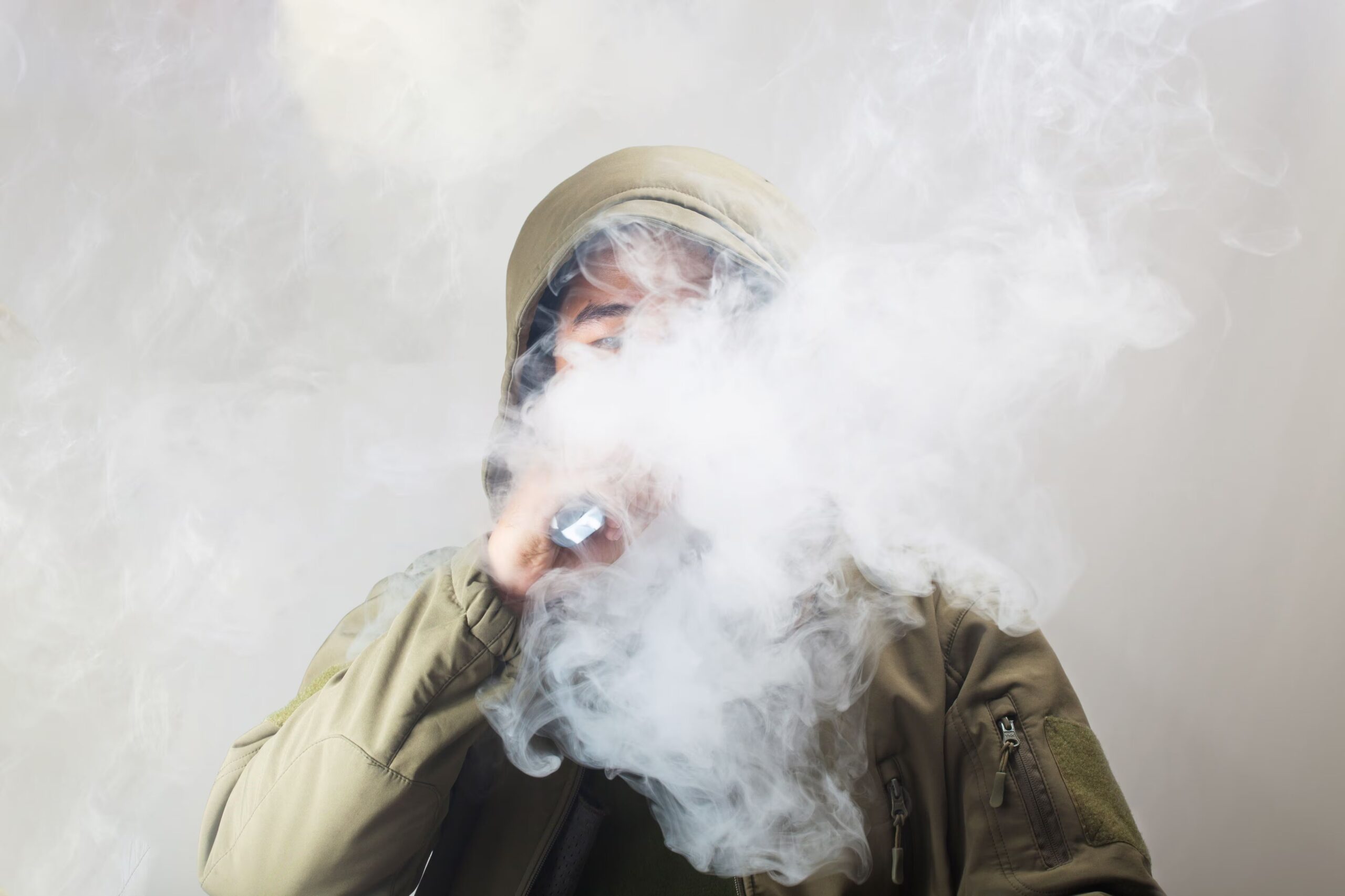
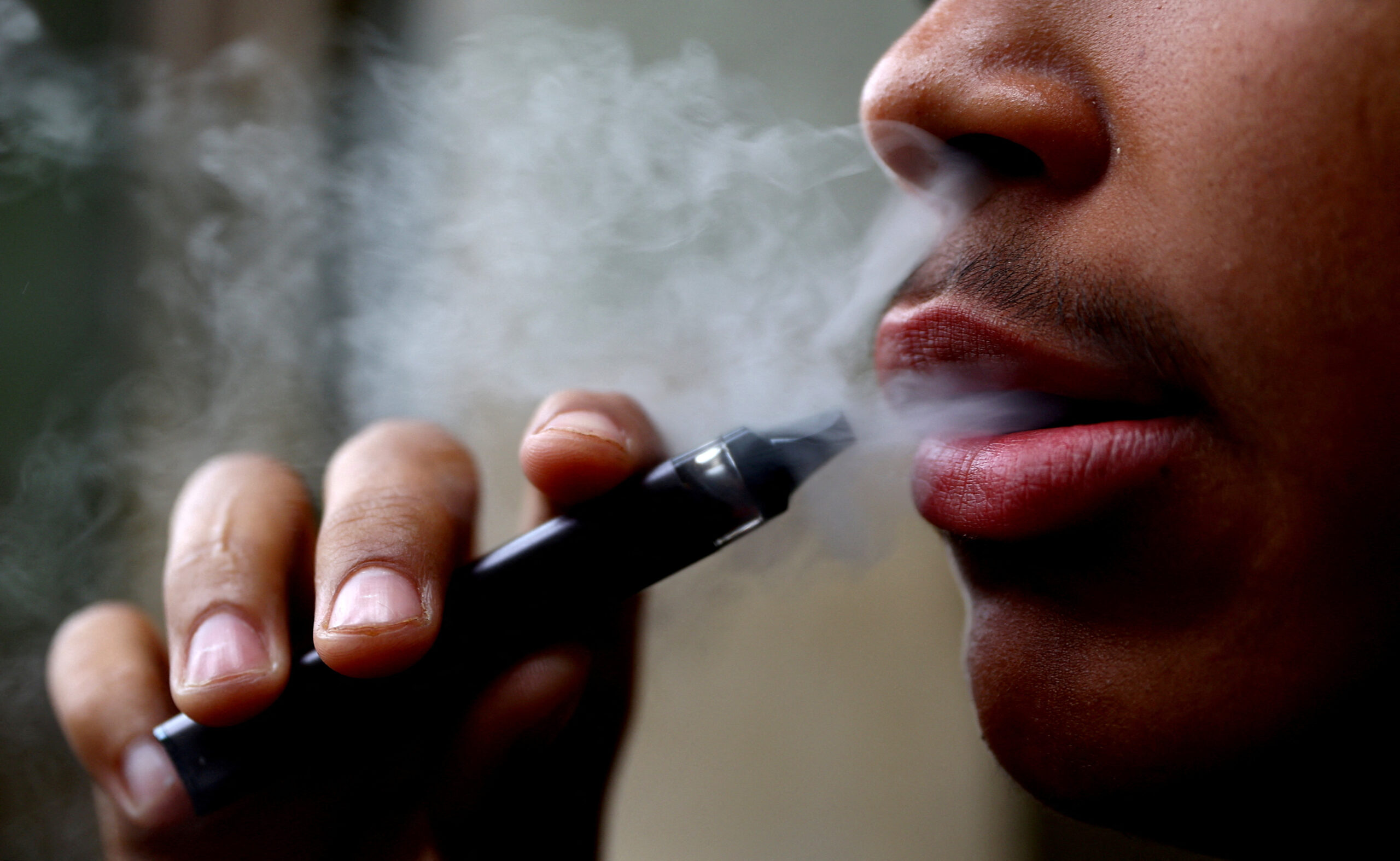
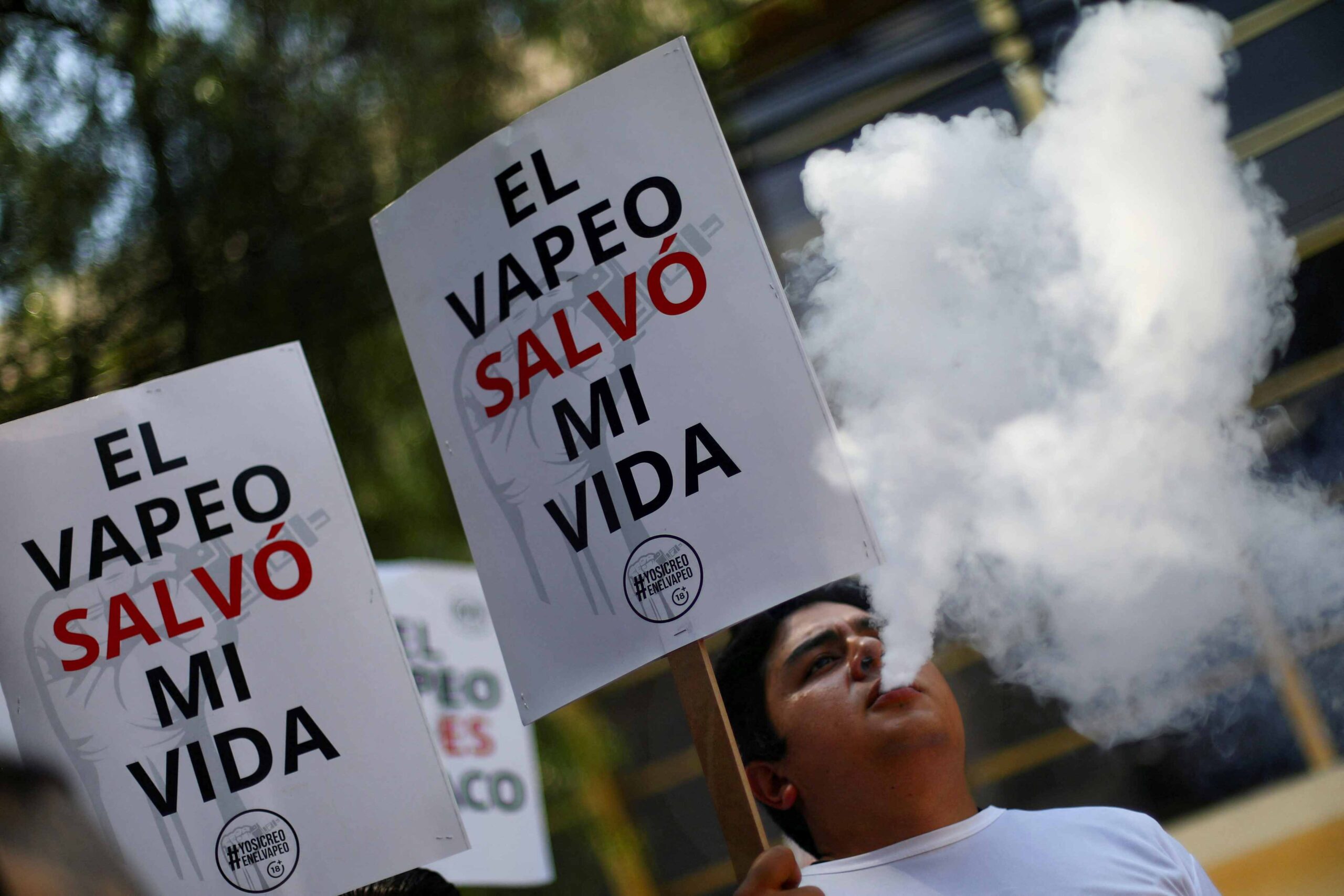
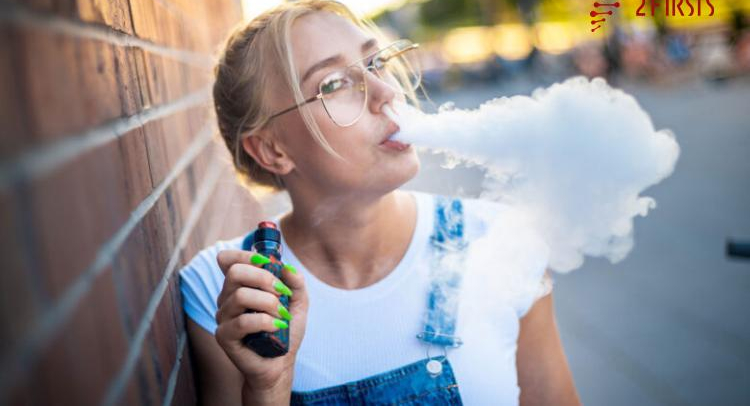
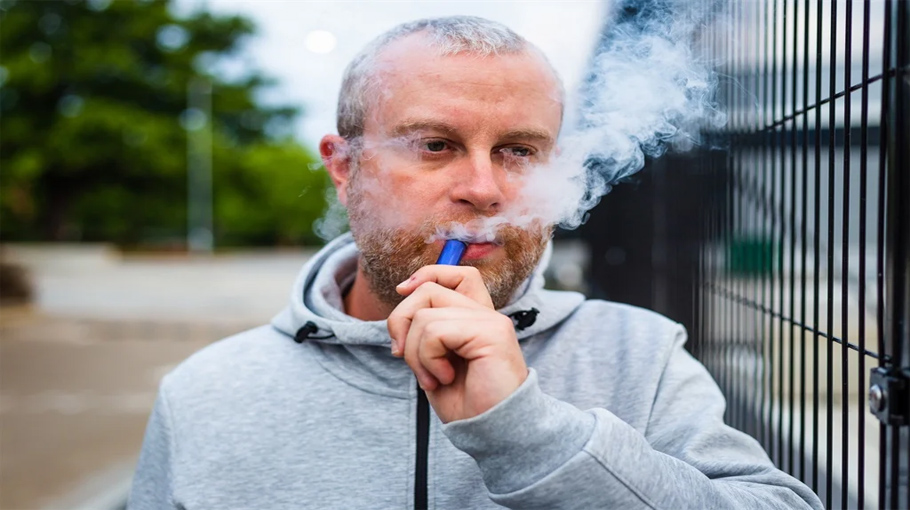
The landscape of smoking regulations is evolving globally, and Vietnam is no exception. In recent developments, the Vietnamese government is contemplating the imposition of new tax regulations specifically targeting e-cigarettes. This move signifies a significant shift in governmental policy towards vaping products and aims to address various concerns surrounding their use and impact on public health.
The Rationale Behind the Proposed Tax Regulations
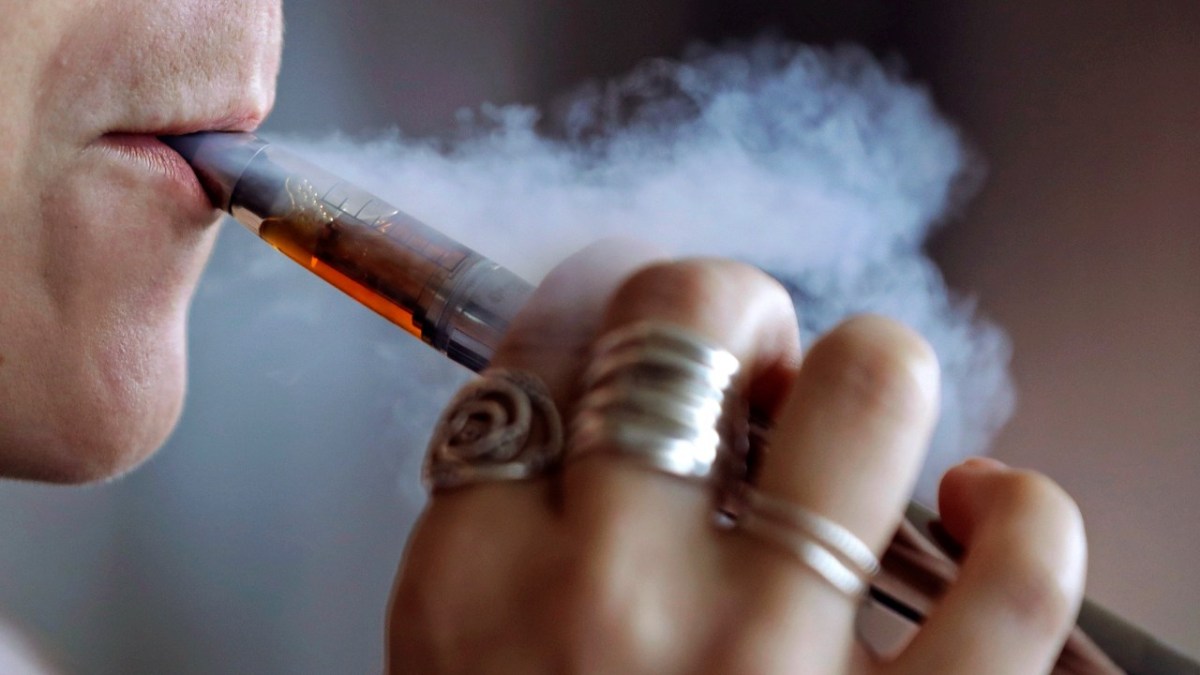
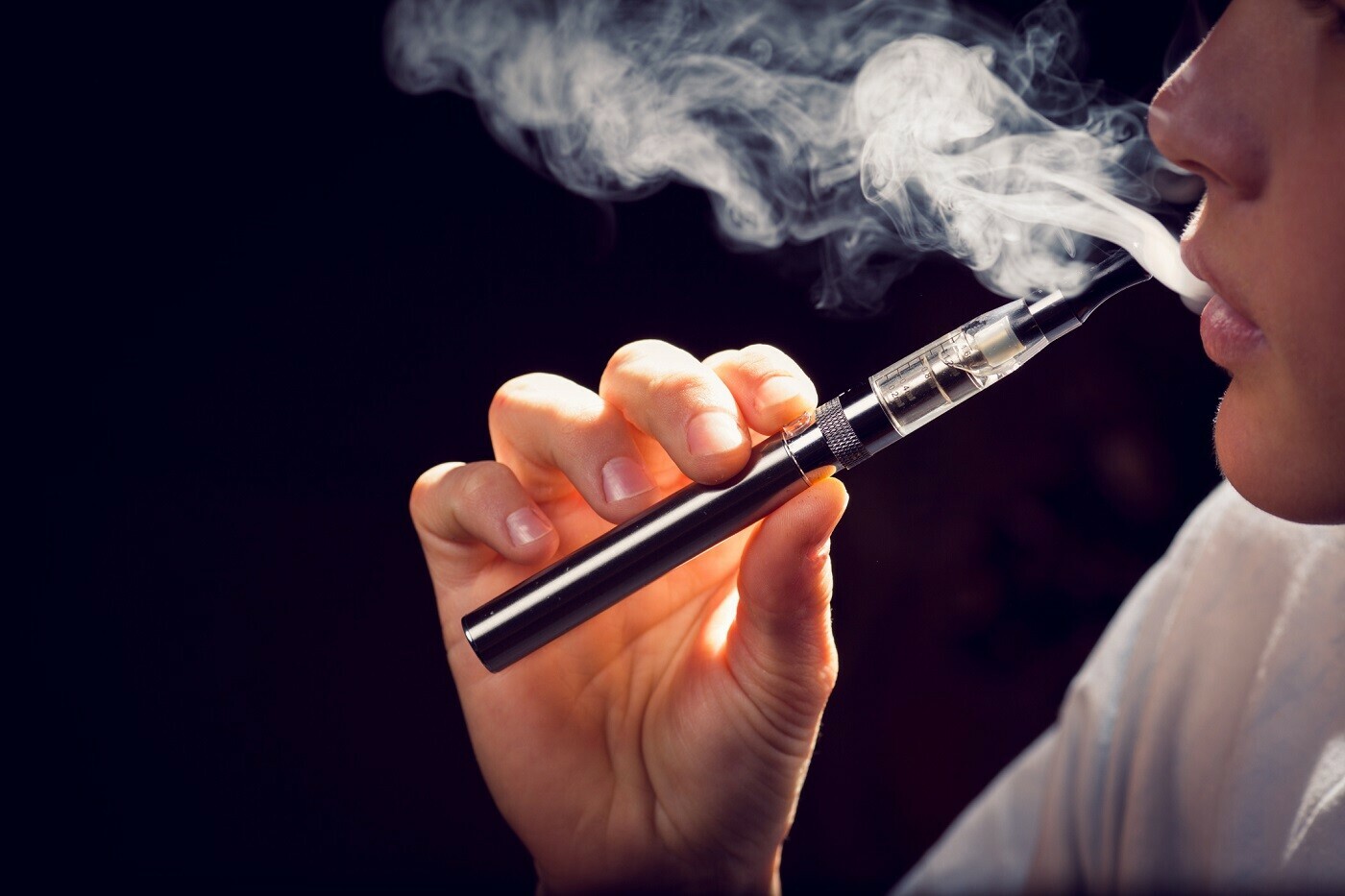
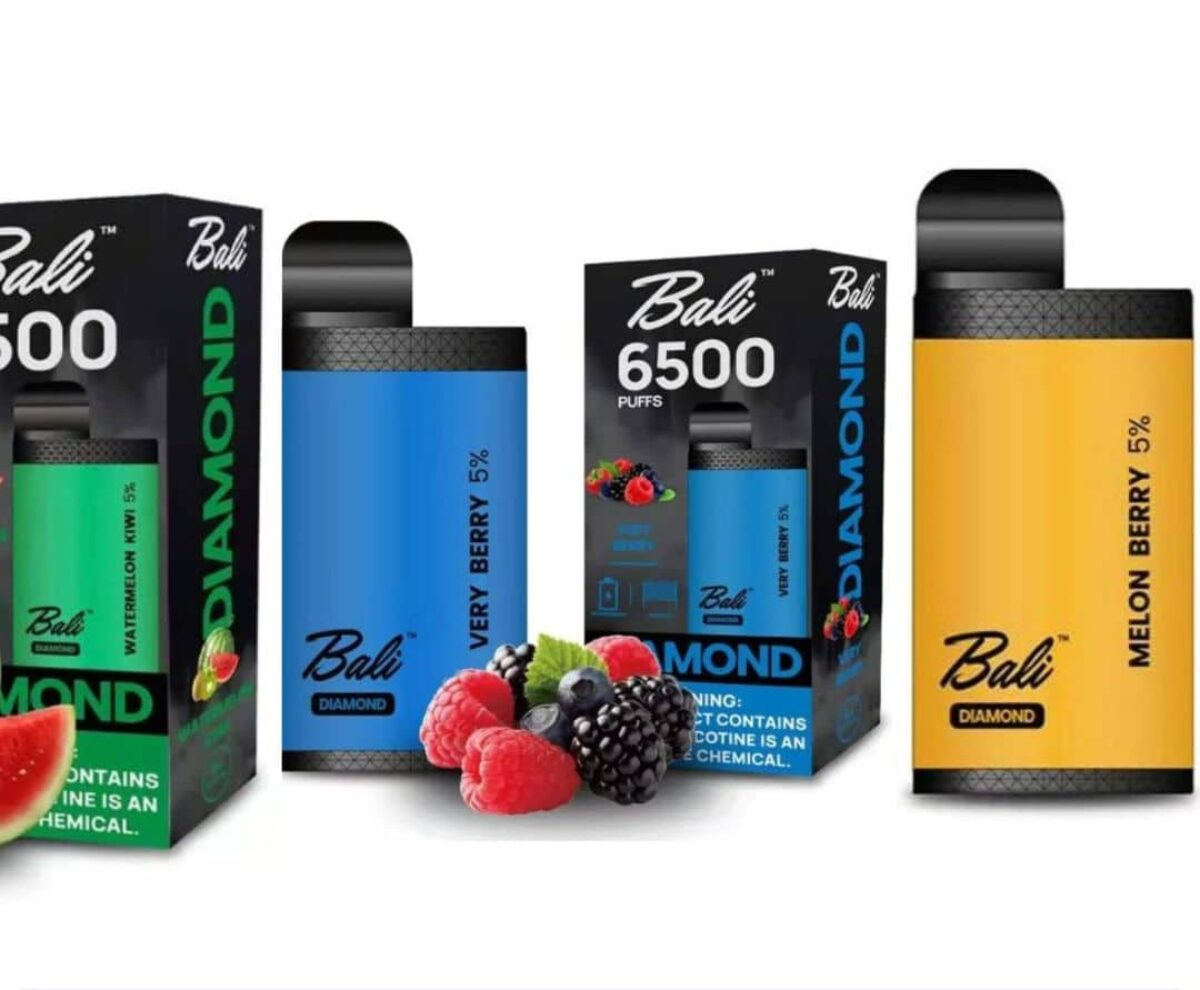
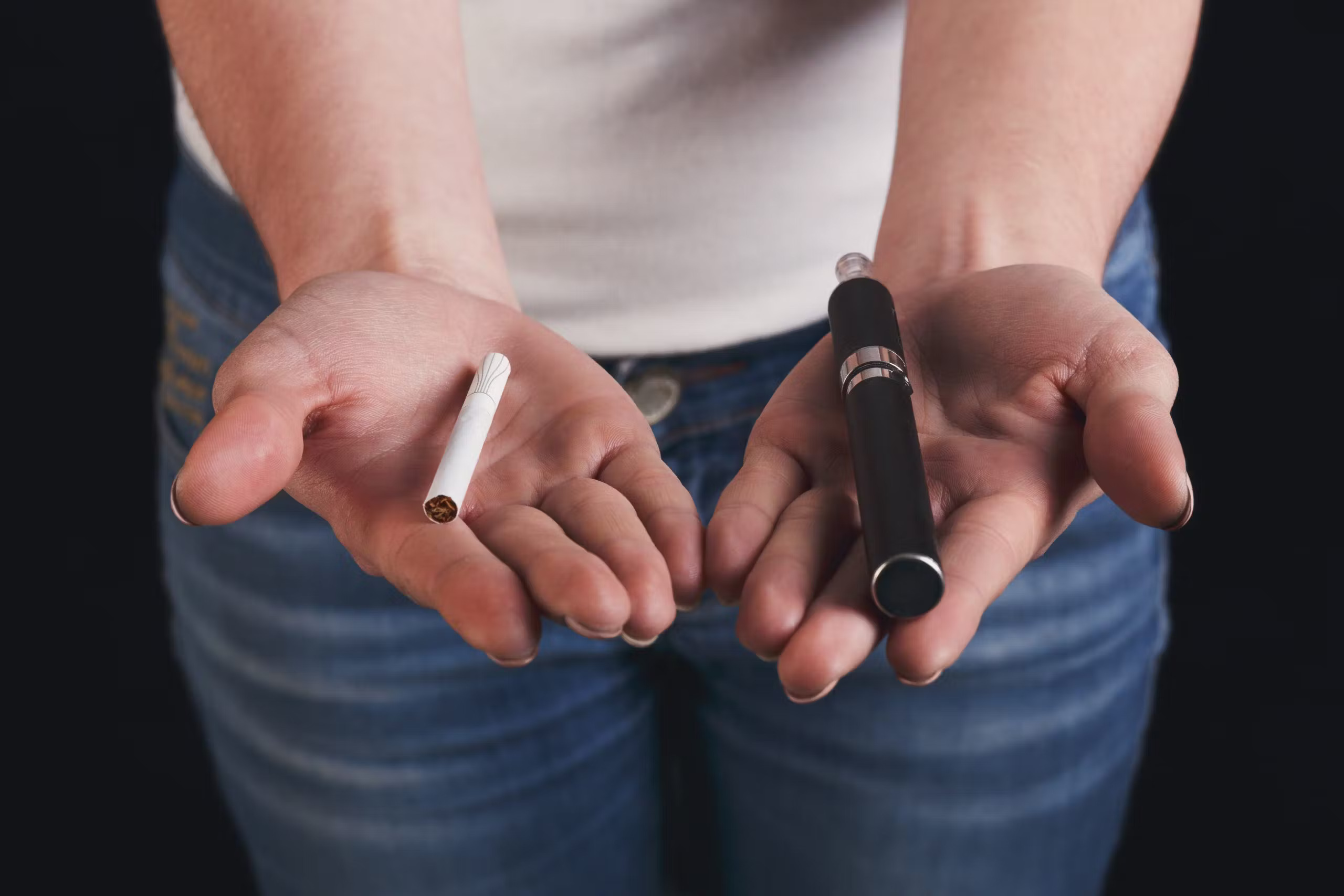
The proposed tax regulations on e-cigarettes in Vietnam stem from several key considerations. Firstly, there is growing evidence suggesting that e-cigarettes pose health risks similar to traditional tobacco products. While marketed as a safer alternative, these devices still contain harmful substances and additives that can have adverse effects on users’ health over the long term.
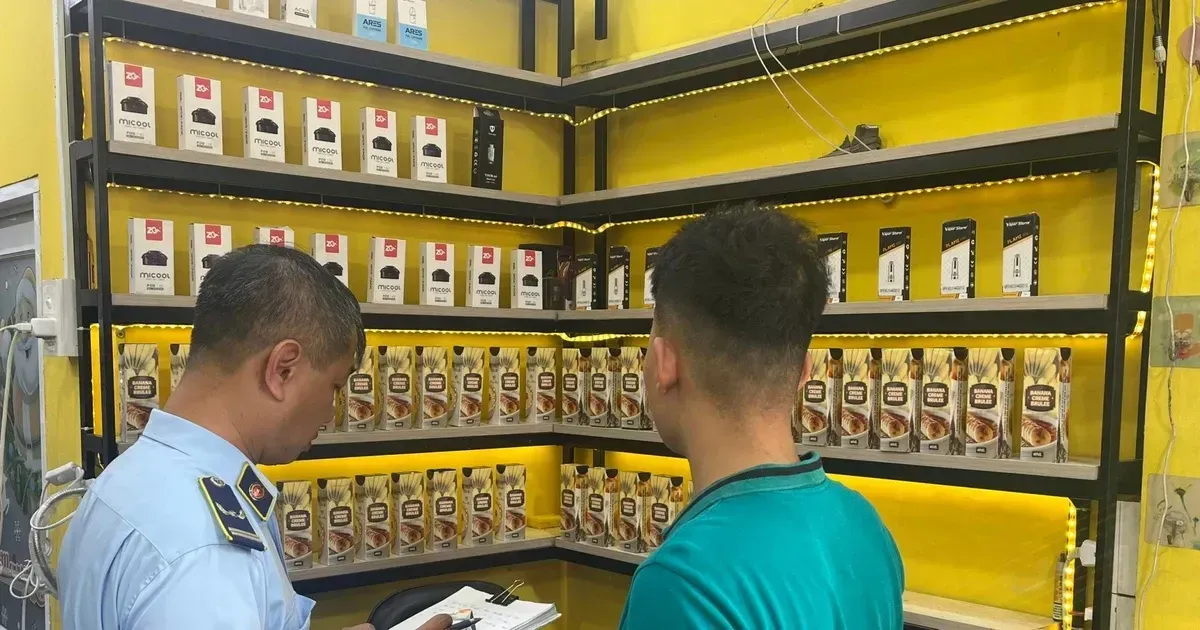
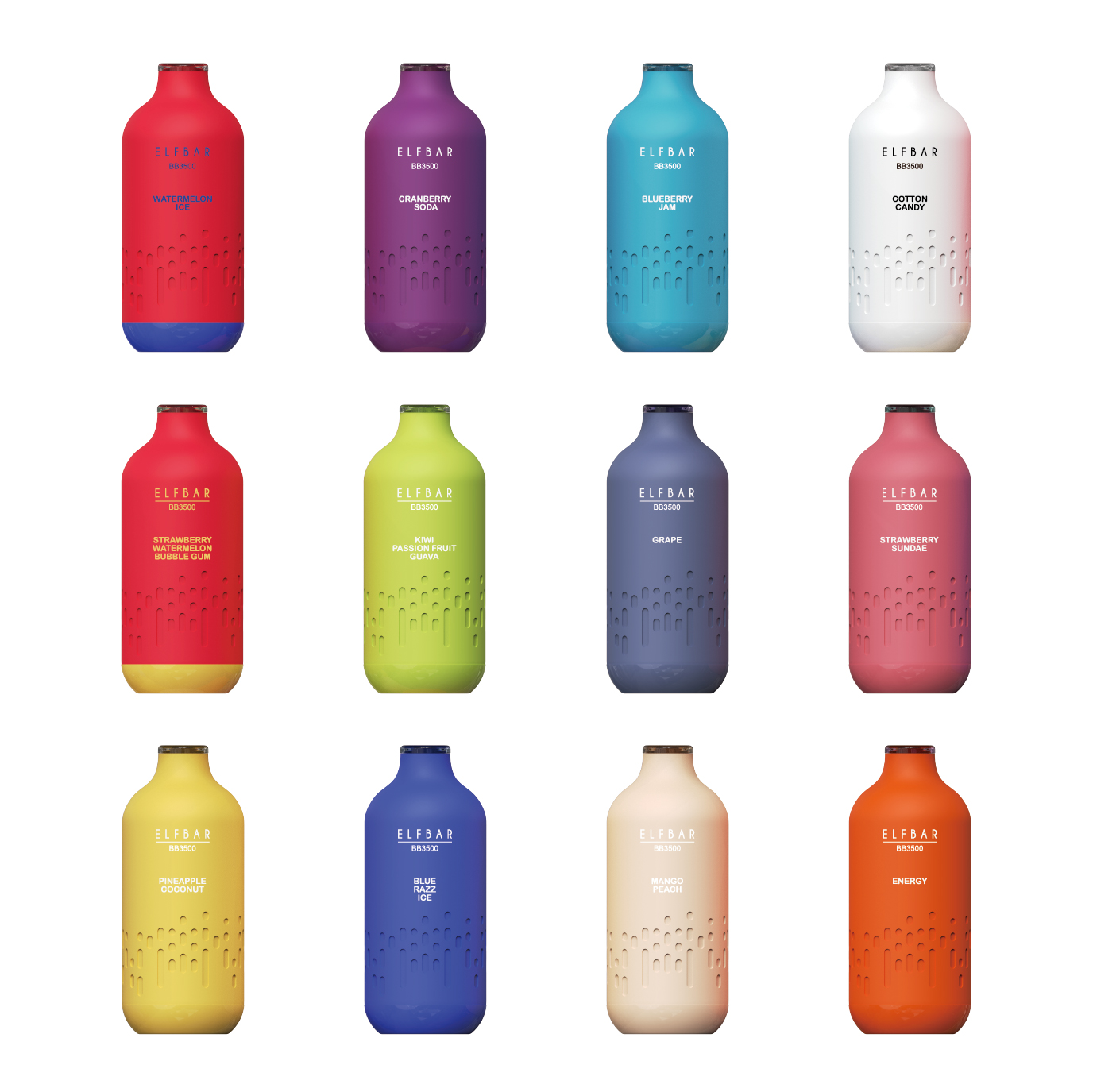
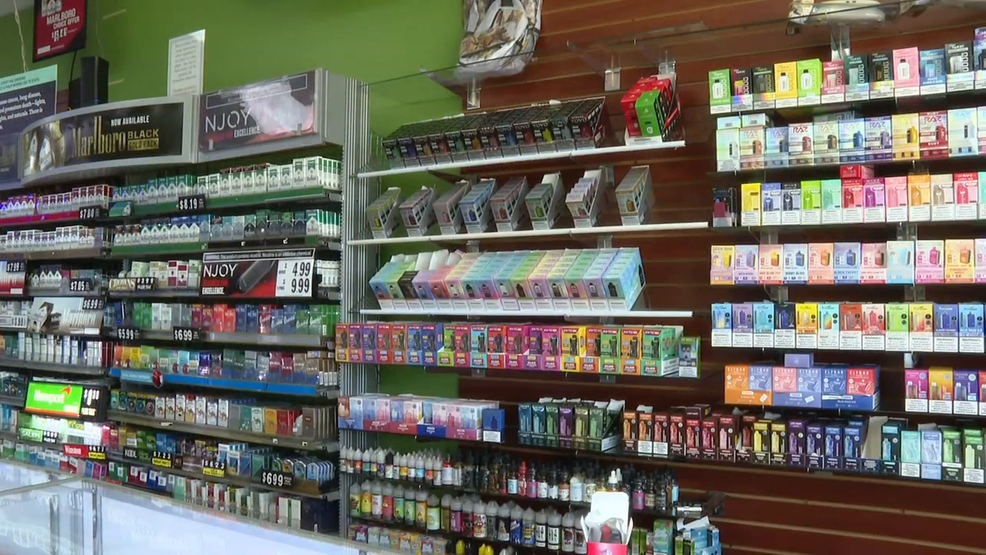
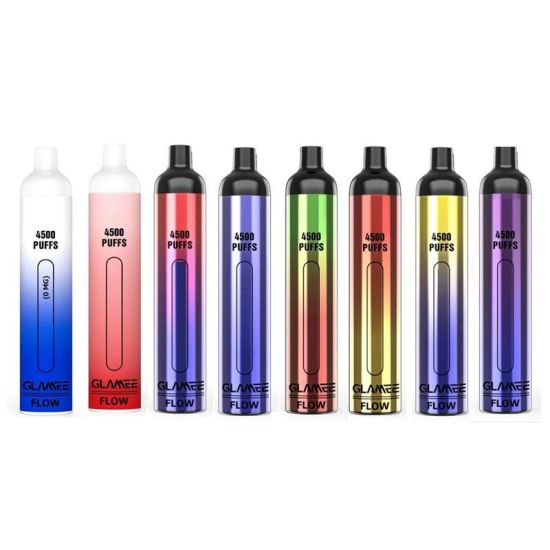
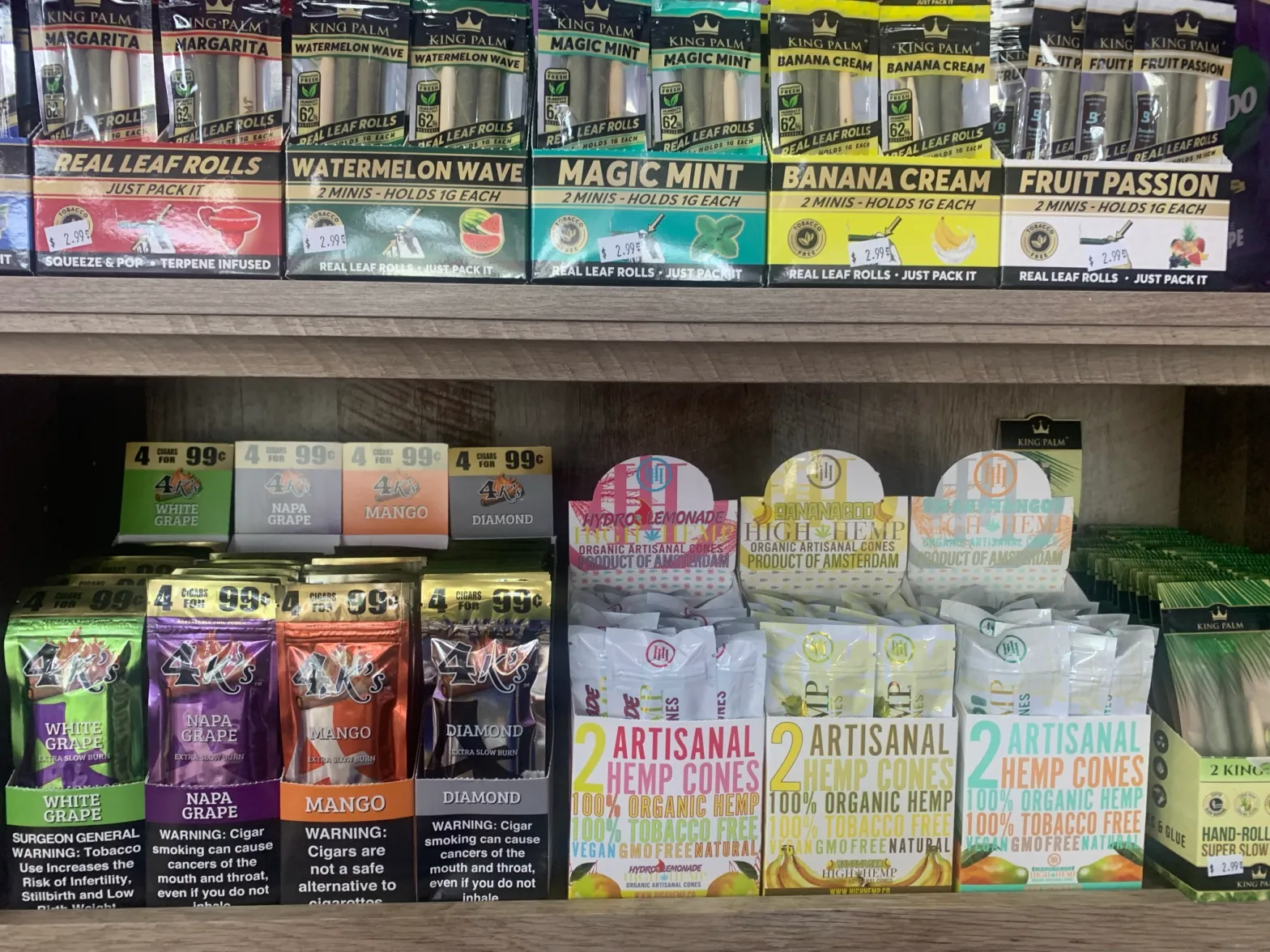
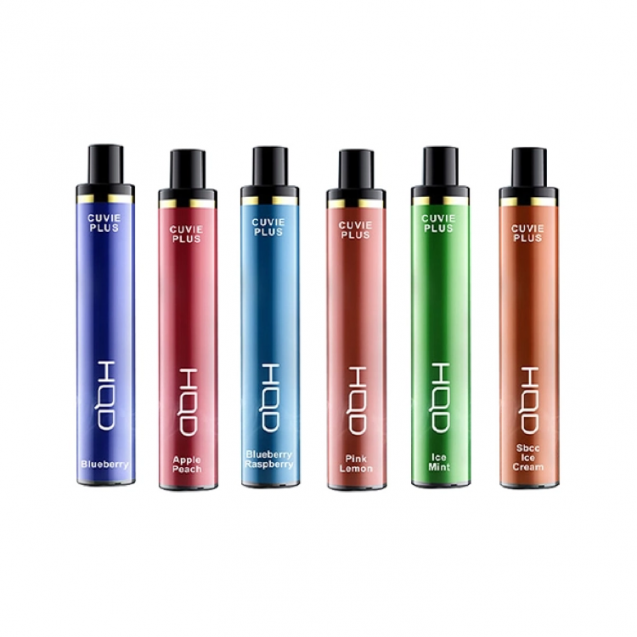
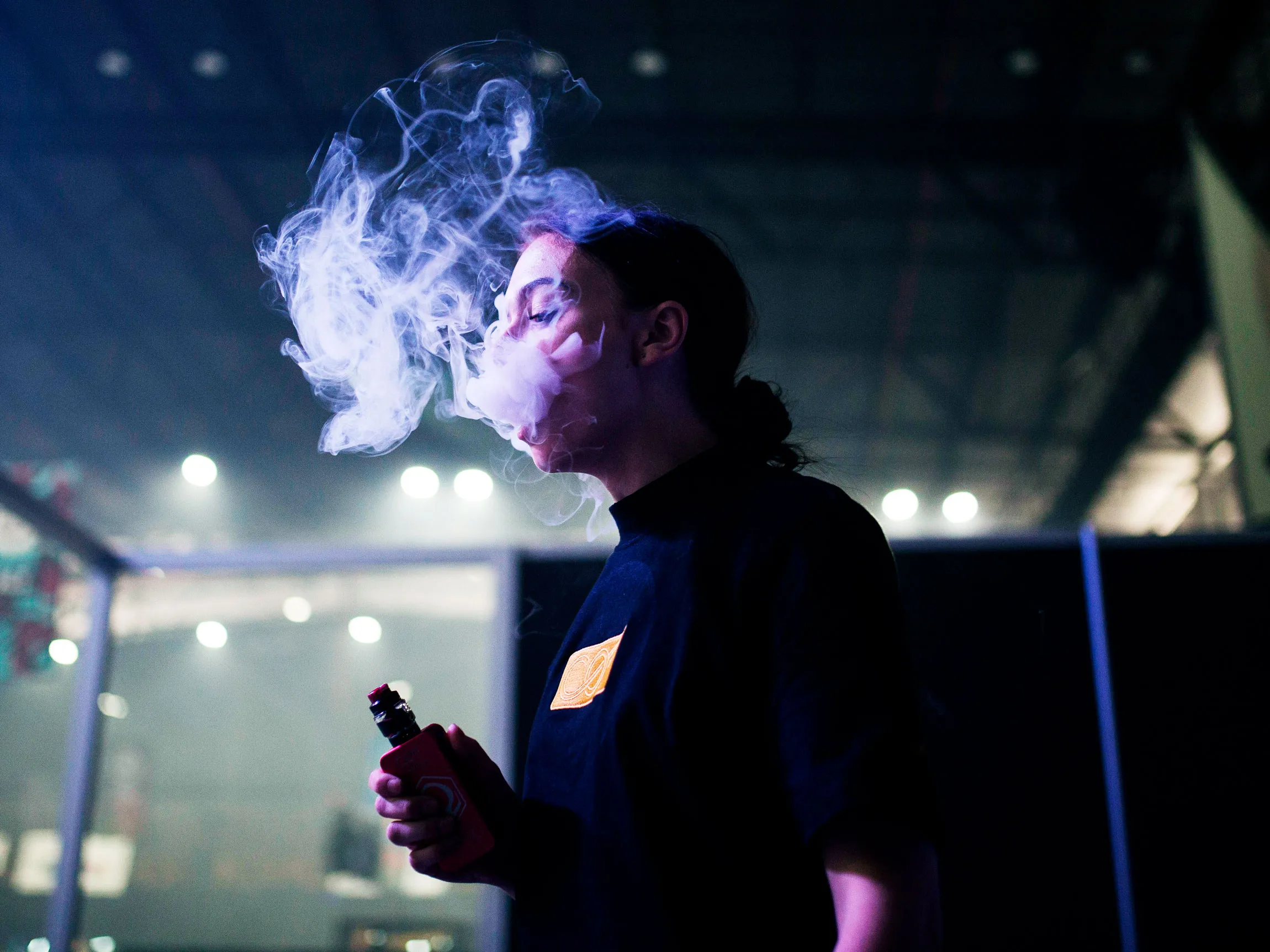
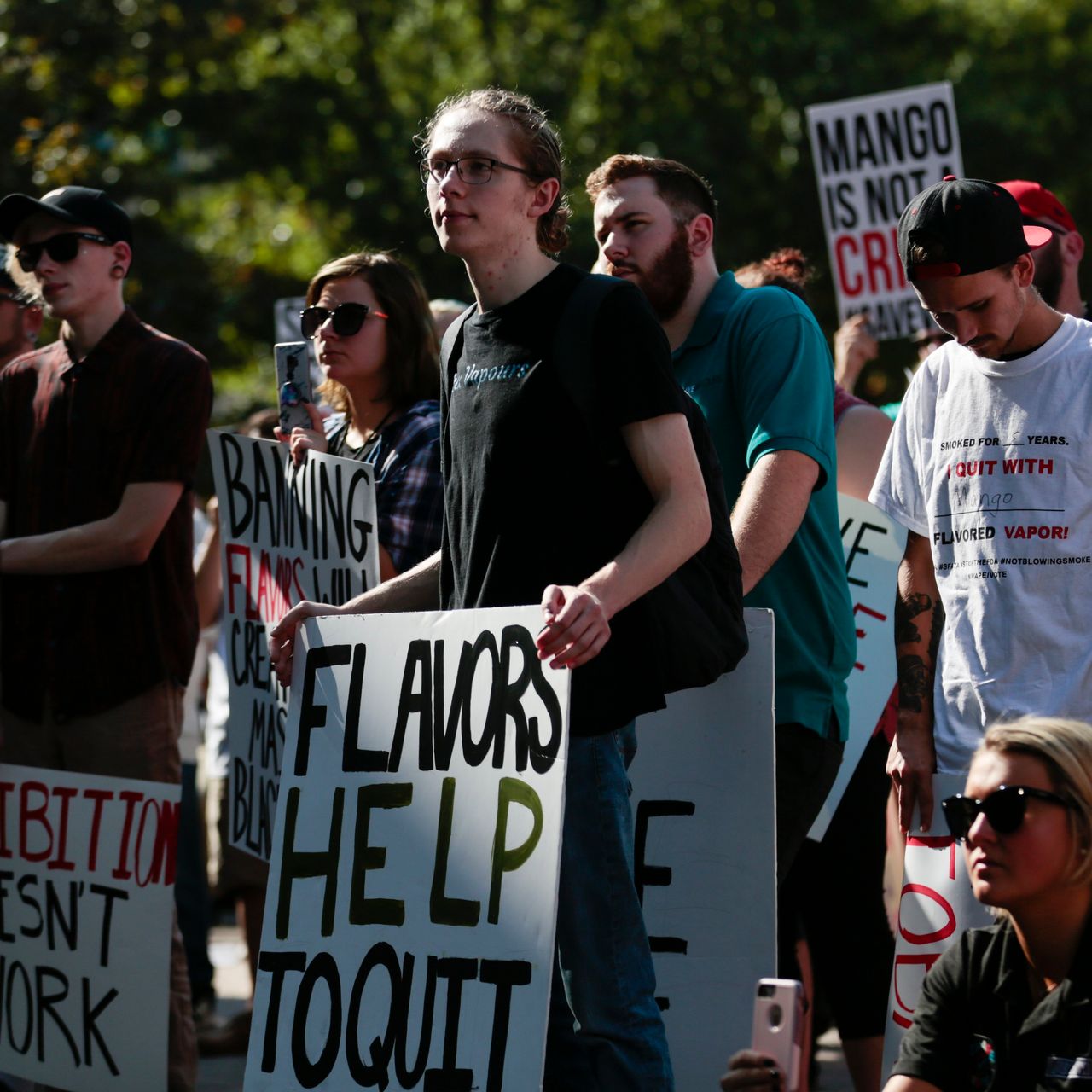
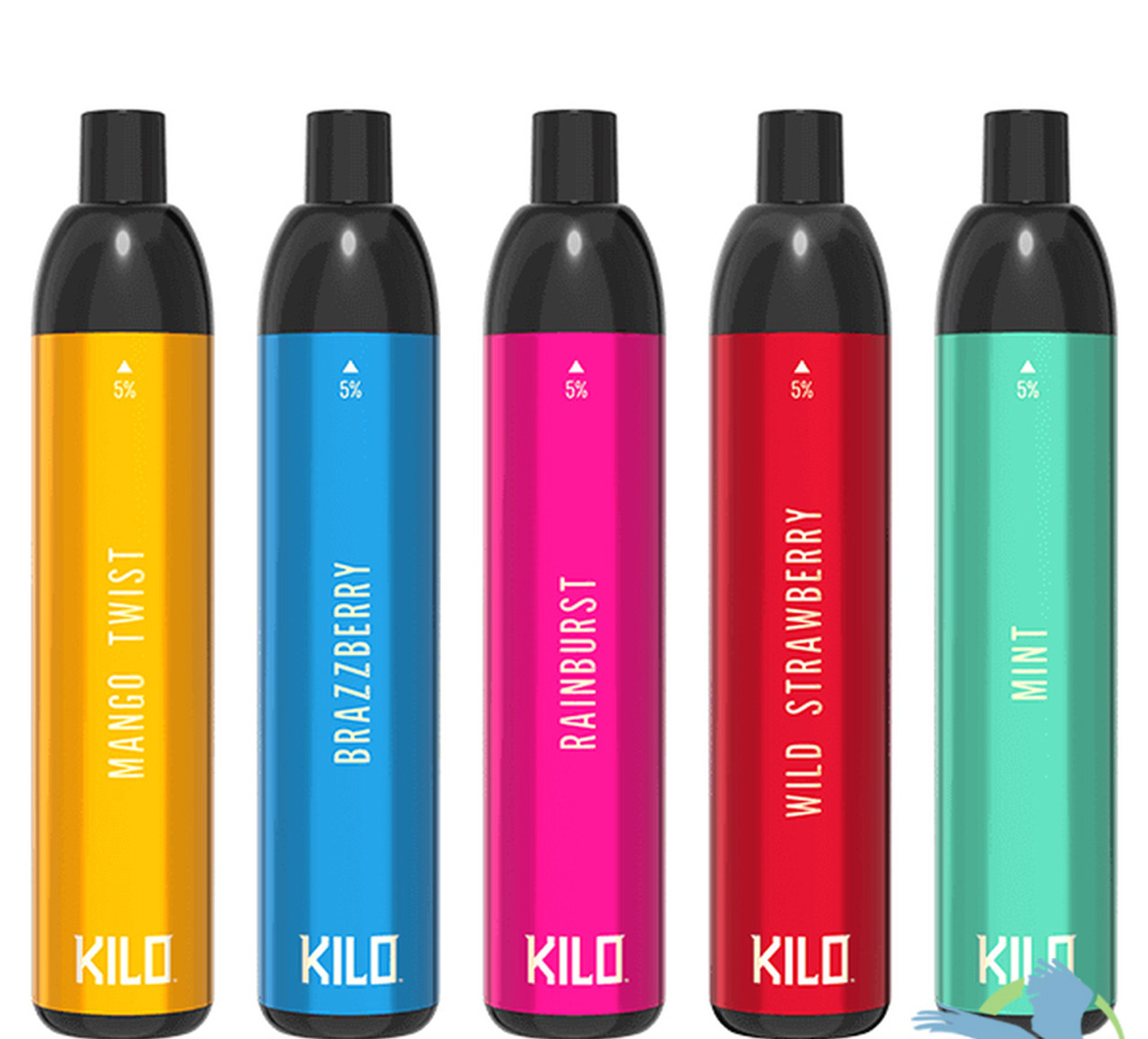
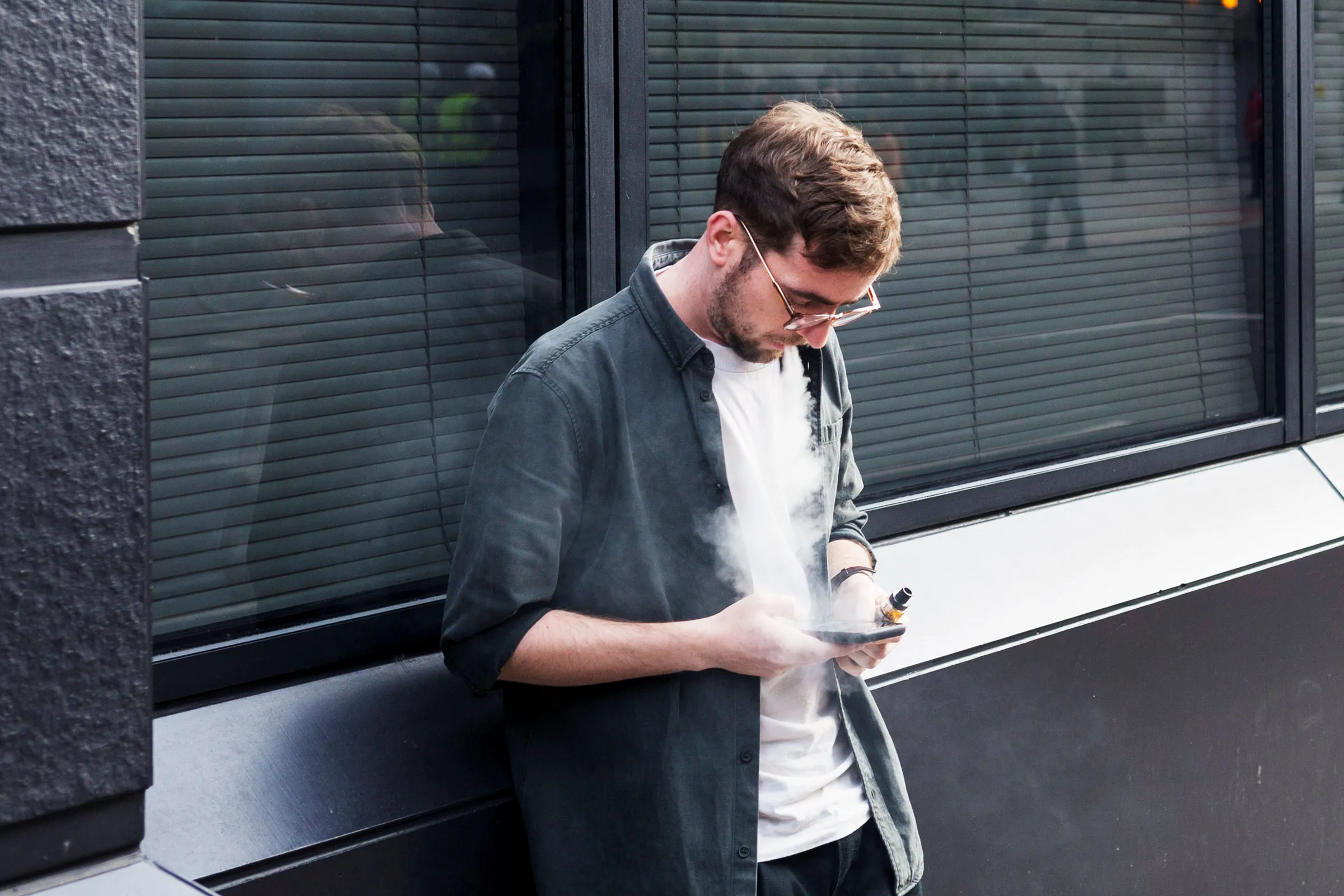
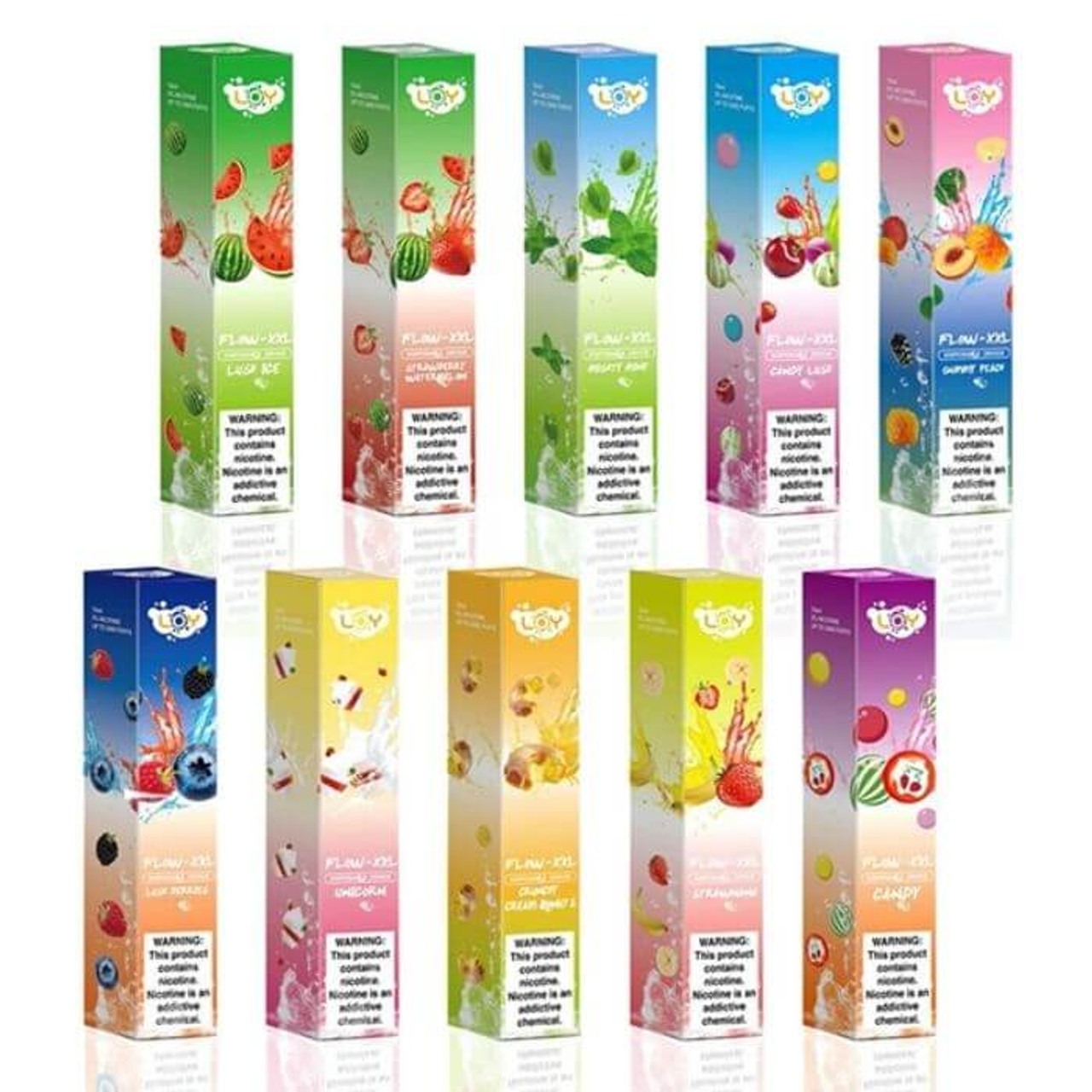
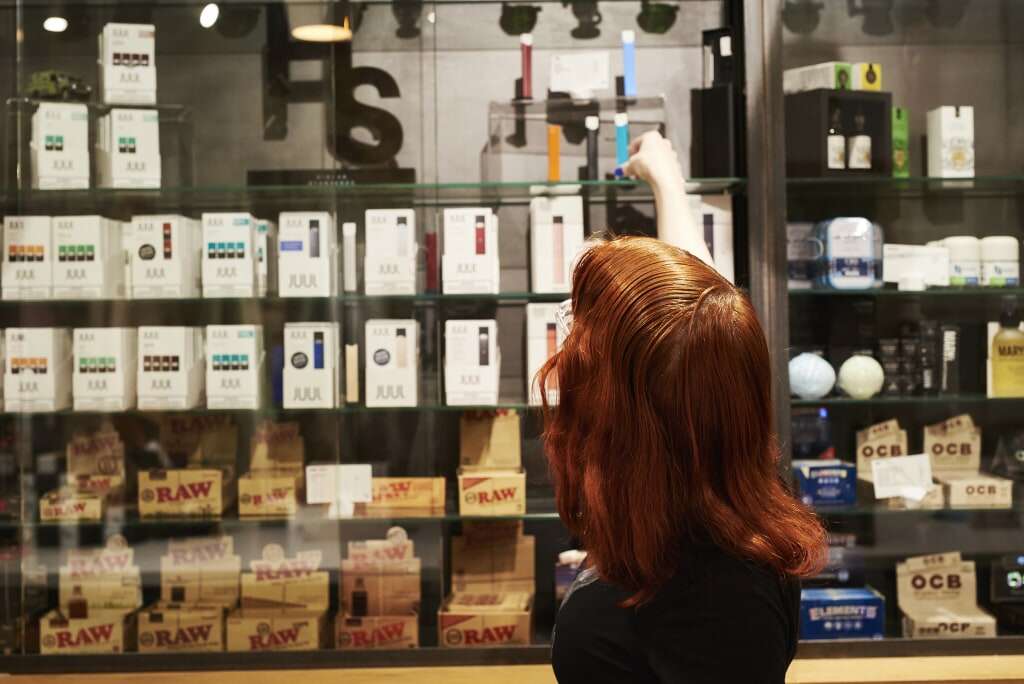
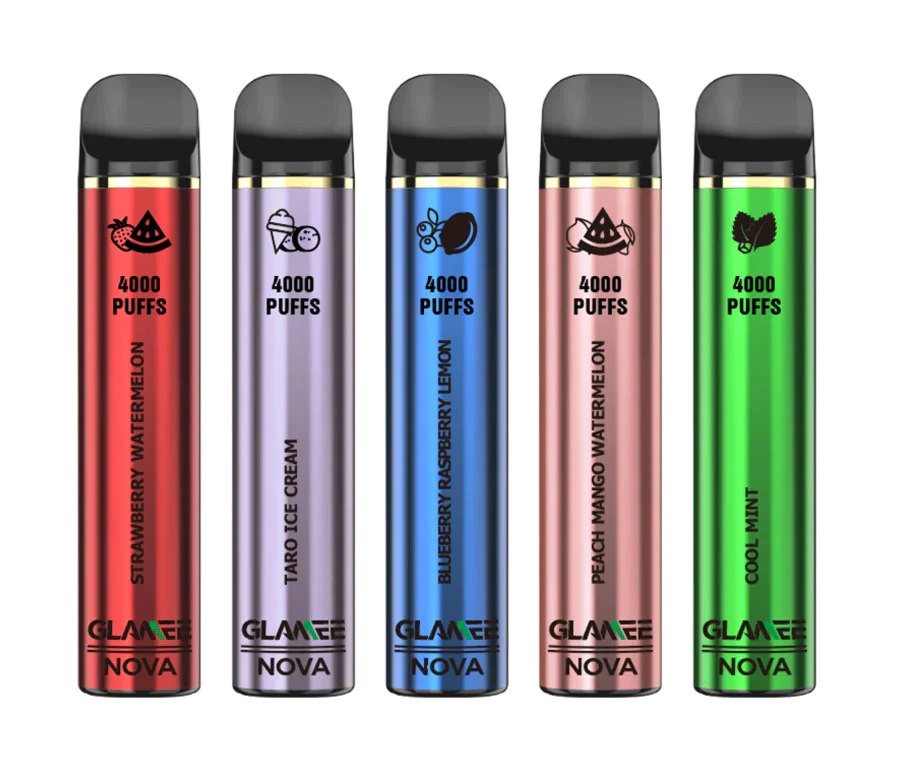
Secondly, there are concerns about the increasing prevalence of e-cigarette use among young people in Vietnam. E-cigarettes come in a variety of appealing flavors and designs, making them attractive to adolescents and young adults. The accessibility and perceived novelty of these products have raised alarms among health officials who fear a potential surge in nicotine addiction and related health issues among the youth population.
Furthermore, the government aims to mitigate the potential economic burden associated with treating illnesses related to e-cigarette use. By imposing taxes on these products, policymakers hope to generate revenue that can be allocated towards healthcare initiatives aimed at addressing smoking-related illnesses and promoting public health education and awareness campaigns.
Potential Impact on Consumers and Industry Players
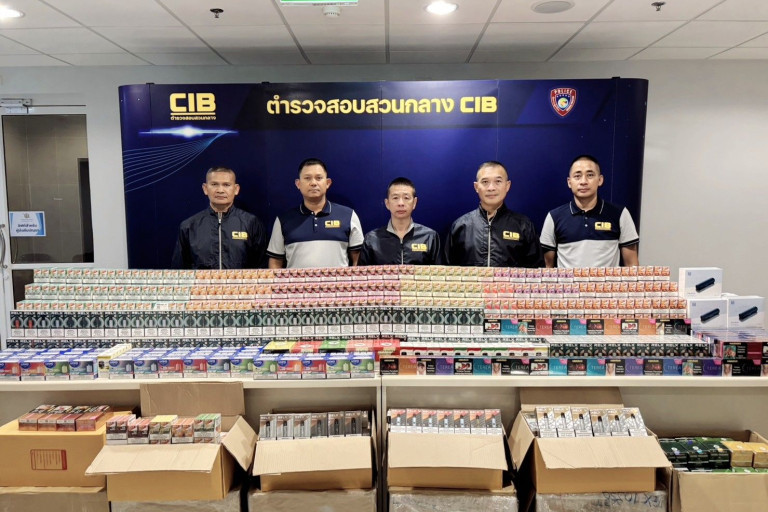
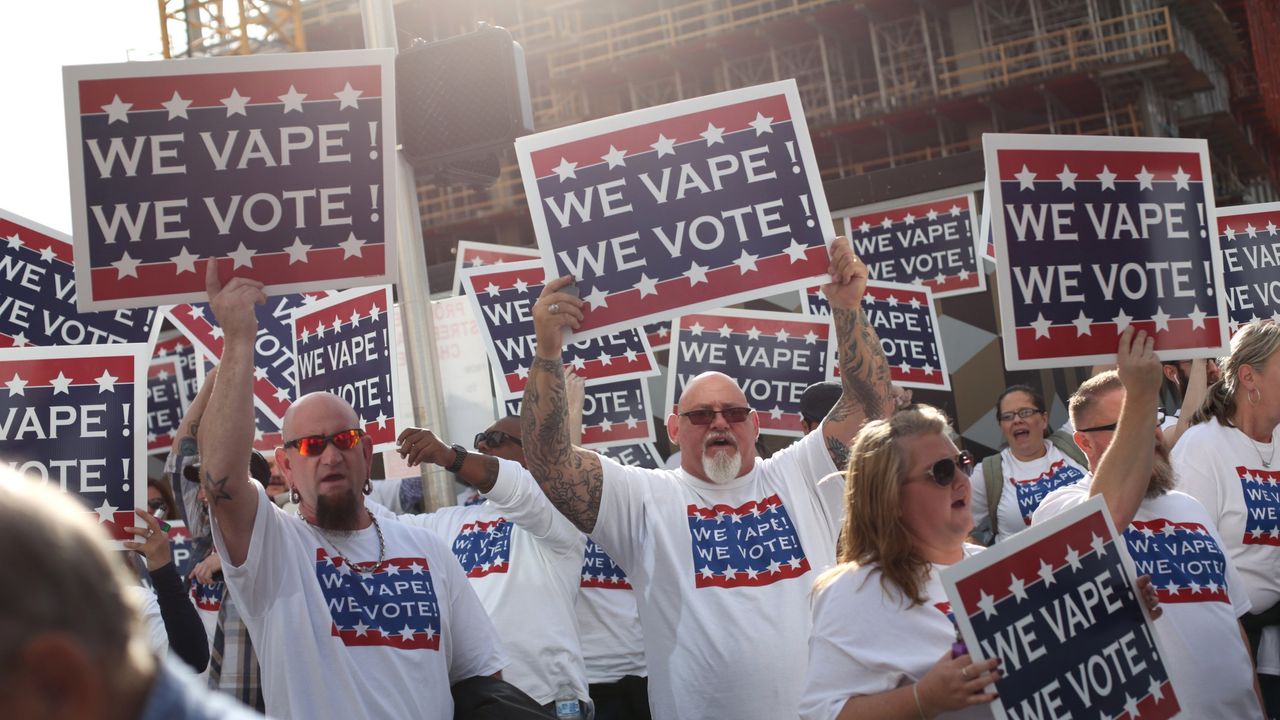
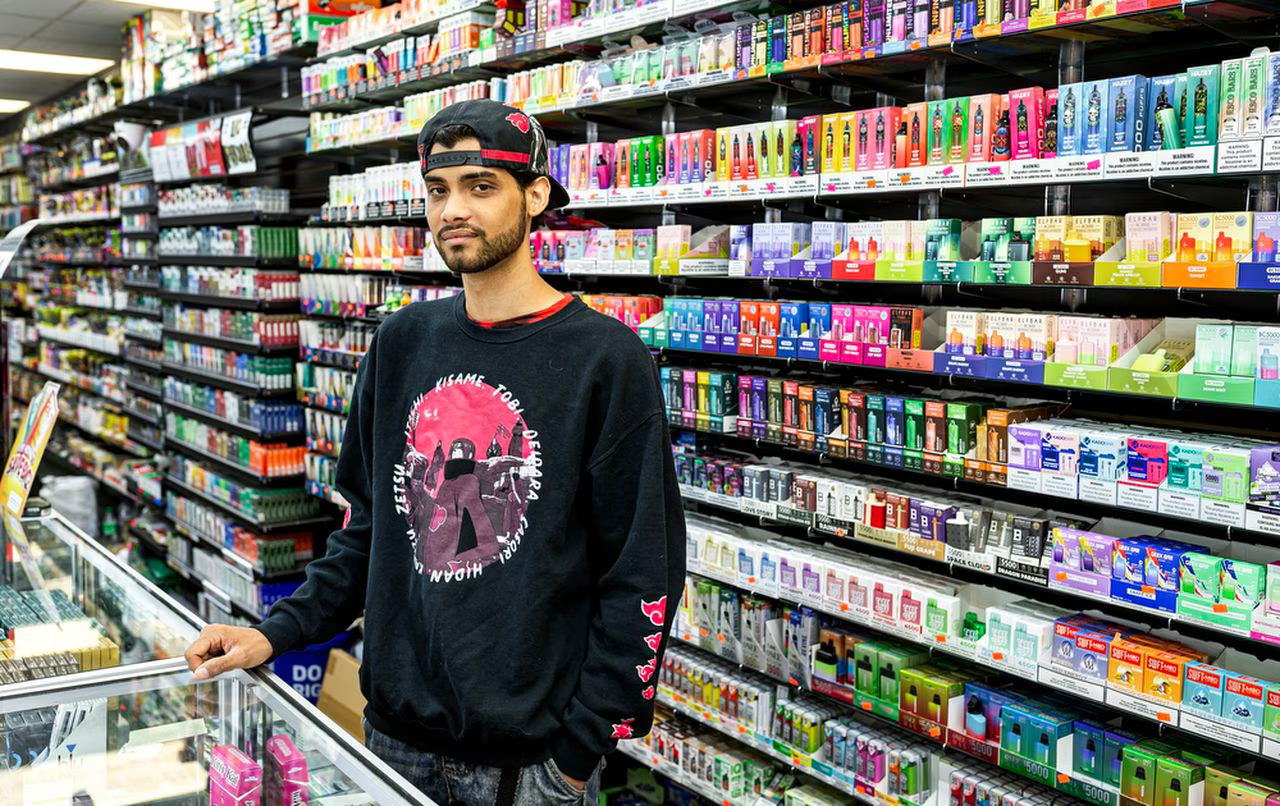
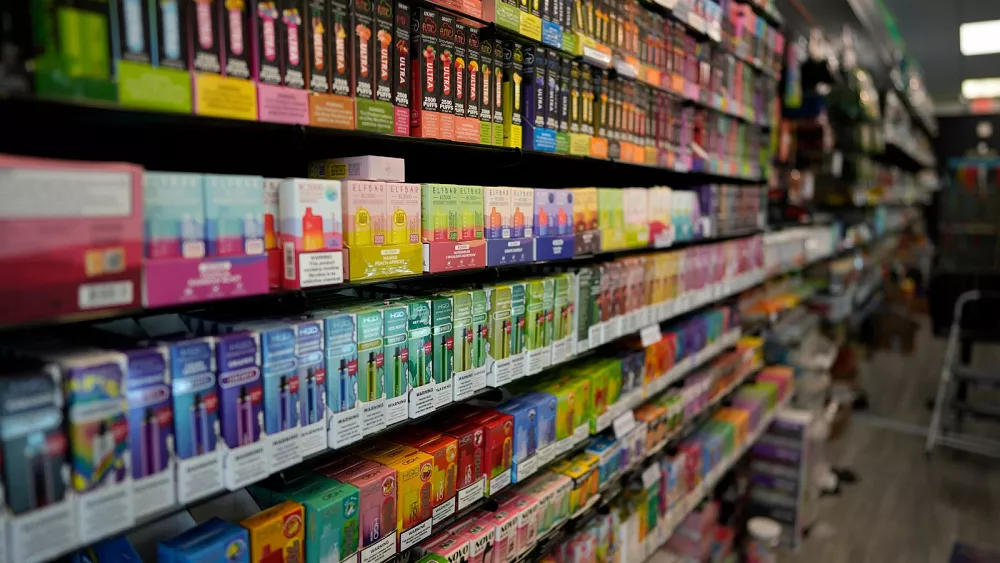
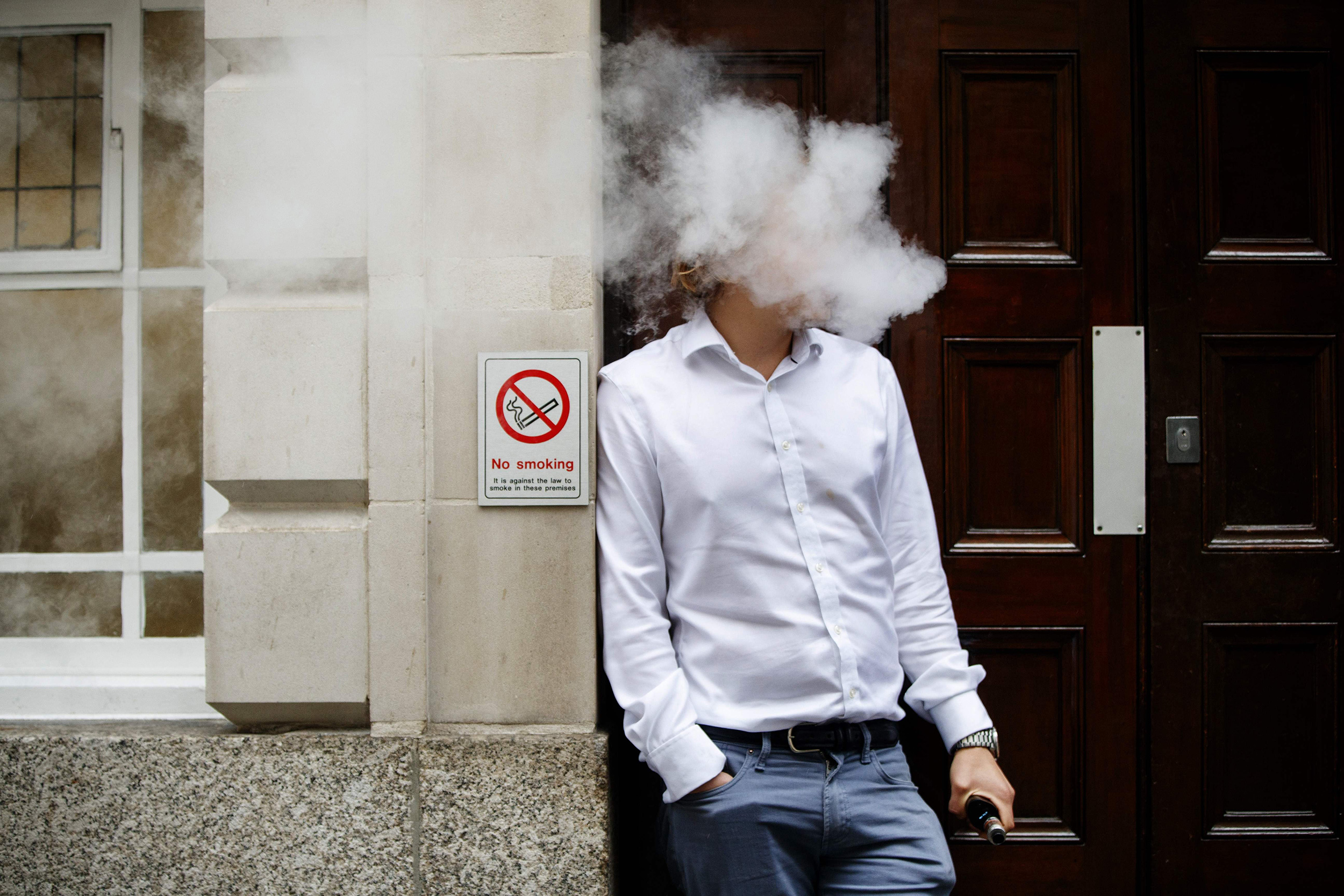
If implemented, the new tax regulations could have significant implications for both consumers and industry players in Vietnam’s e-cigarette market. For consumers, the cost of purchasing e-cigarettes is likely to increase, making them less affordable compared to traditional tobacco products. This price hike may serve as a deterrent for some users, potentially reducing overall consumption rates.
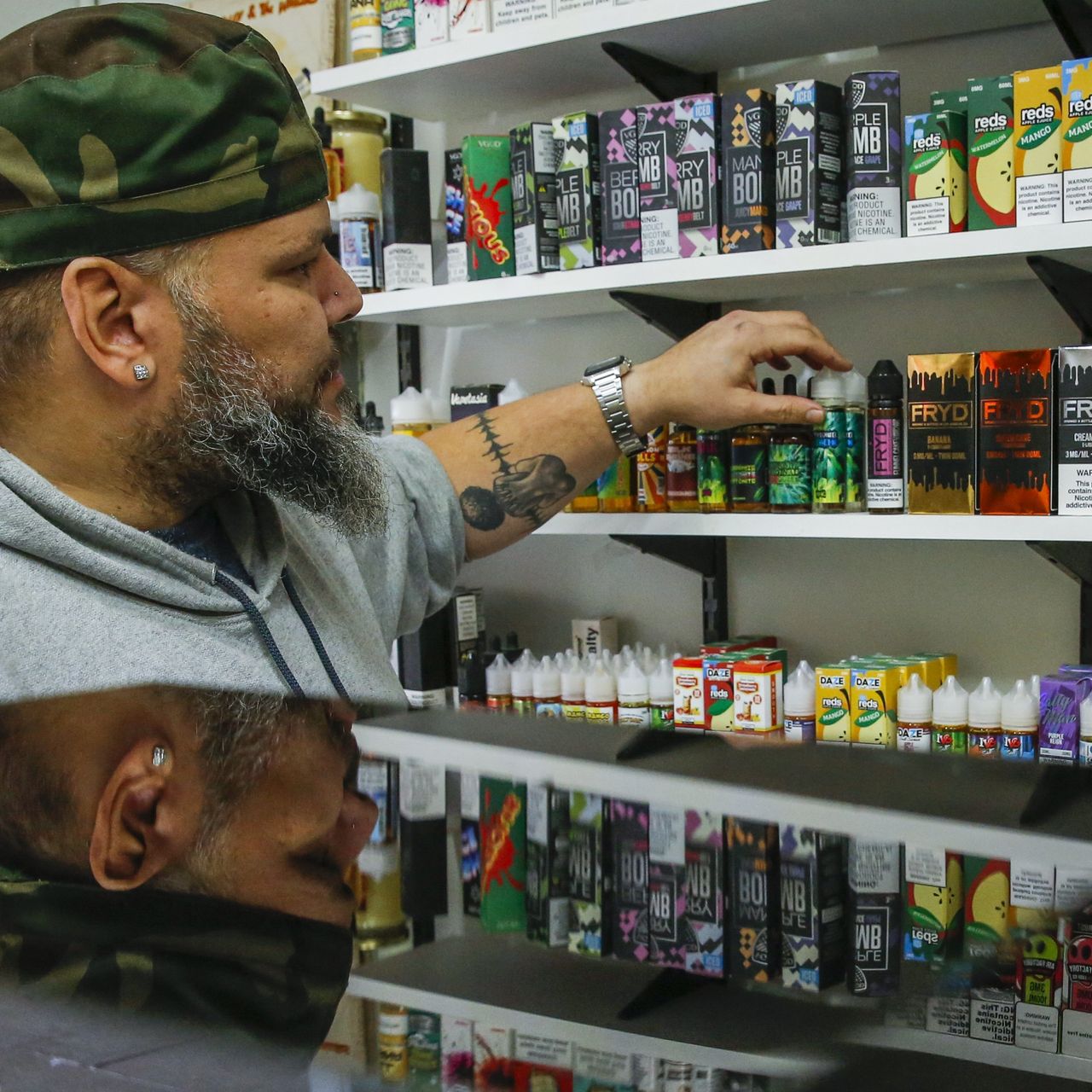
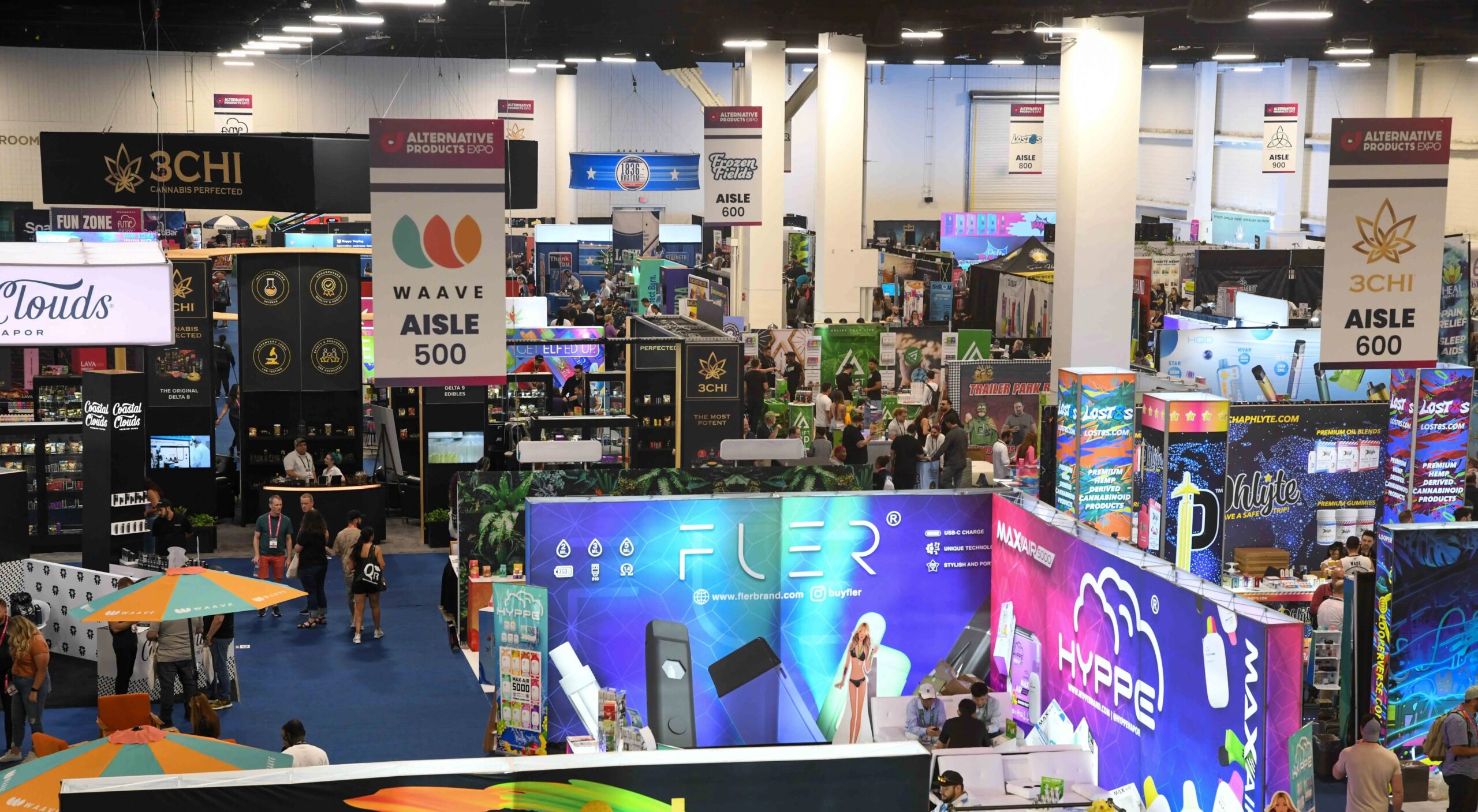
On the other hand, e-cigarette manufacturers and retailers may face challenges in adapting to the new tax regime. Compliance with tax regulations requires additional administrative efforts and may result in higher operating costs for businesses. Moreover, the imposition of taxes could reshape the competitive landscape within the industry, potentially favoring larger players with the resources to absorb the additional financial burden.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Vietnamese government’s consideration of new tax regulations on e-cigarettes reflects a broader effort to address public health concerns and regulate the consumption of alternative tobacco products. While the proposed measures aim to curb the rising popularity of e-cigarettes and mitigate associated health risks, they also raise questions about their potential impact on consumers and industry dynamics.
As discussions surrounding e-cigarette regulation continue, it is essential for policymakers to consider evidence-based approaches that balance public health objectives with economic considerations. Ultimately, the effectiveness of the proposed tax regulations will depend on their ability to deter e-cigarette use while ensuring equitable access to smoking cessation resources and support services for those affected by nicotine addiction.





































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































0